Photovoltaic Greenhouses: Harnessing Solar Power to Sustain Aquaponic Systems
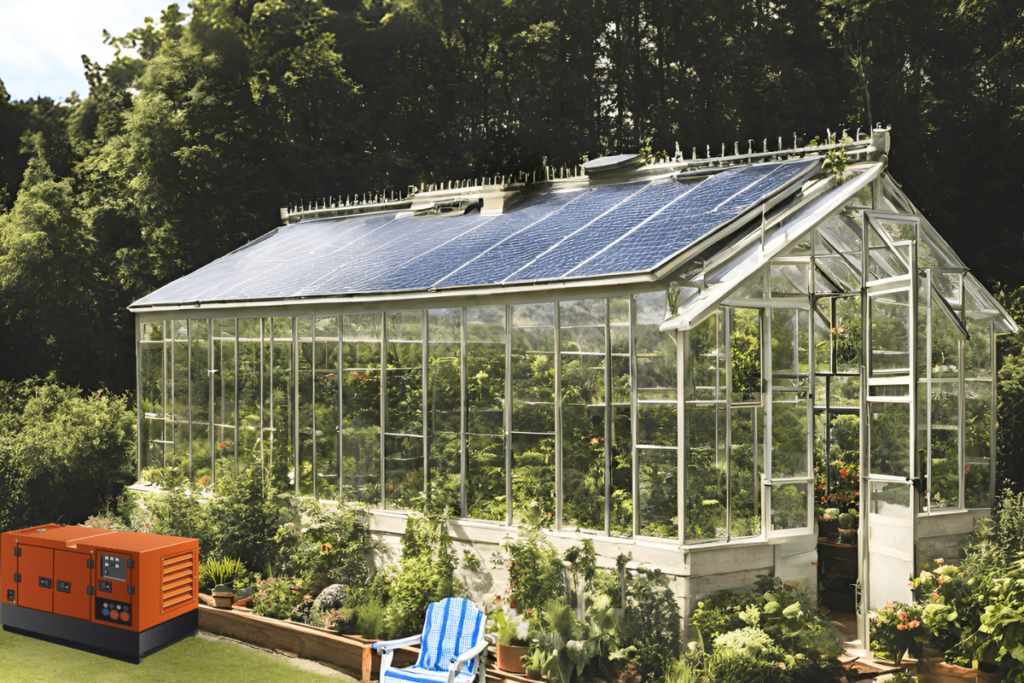

As the world continues to shift towards sustainable and renewable energy sources, innovative approaches to agriculture and food production are becoming increasingly essential. One such approach is the use of photovoltaic (PV) greenhouses, which combine solar energy generation with traditional greenhouse farming. By integrating photovoltaic panels into greenhouse structures, it is possible to convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power various systems inside the greenhouse, including pumps for aquaponics. This fusion of technology not only makes the greenhouse self-sufficient in terms of energy but also promotes sustainable farming practices.
What Are Photovoltaic Greenhouses?
Photovoltaic greenhouses are essentially greenhouses equipped with solar panels that capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. Unlike traditional greenhouses that allow all sunlight to pass through the transparent roof and walls to nourish plants, photovoltaic greenhouses strategically position solar panels to capture only a portion of the sunlight. The rest of the light penetrates the structure, providing the necessary energy for photosynthesis.

The solar panels used in these greenhouses can be placed on the roof, walls, or even integrated into transparent or semi-transparent surfaces, allowing for a balance between energy production and plant growth. The electricity generated can then be used to power various electrical components within the greenhouse, such as heating systems, lighting, and, importantly, pumps for aquaponic systems.

The Role of Aquaponics in Photovoltaic Greenhouses
Aquaponics is a sustainable farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants in water without soil). In an aquaponic system, fish produce waste that is converted by beneficial bacteria into nutrients, which are then absorbed by plants. The plants, in turn, help filter and clean the water, which is recirculated back to the fish tanks. This symbiotic relationship creates a closed-loop system that uses significantly less water than traditional farming methods.
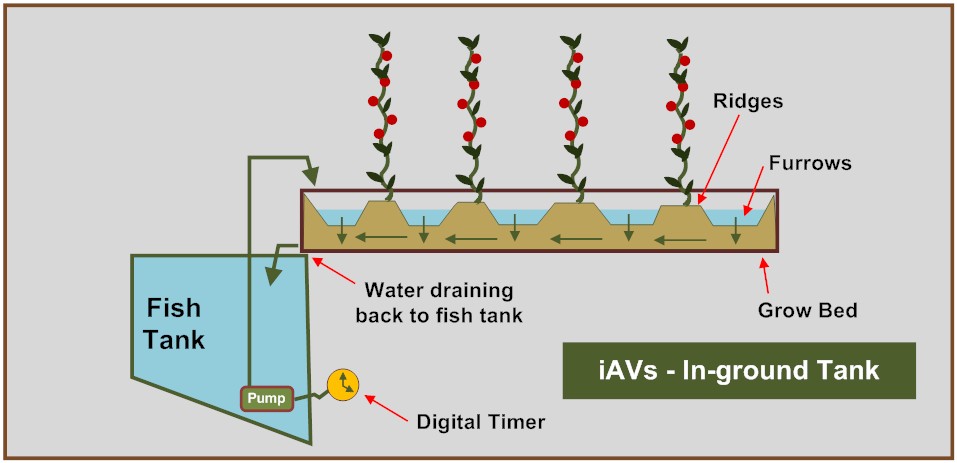
One of the benefits of the aquaponics system is that it recycles water and therefor uses less of it than traditional plants in soil. Since it uses less water, the greenhouse isn’t as much of a liability by blocking new rainwater. Rainwater can be trapped in barrels to use in water exchanges or replacement of water lost through evaporation.
The one need of an aquaponics systems is the requirement of a constant flow of water to transport nutrients to plants and keep the fish healthy. This is where the photovoltaic greenhouse comes into play. By using solar panels to generate electricity, photovoltaic greenhouses can power the pumps needed to circulate water through the system, making the entire setup more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Advantages of Photovoltaic Greenhouses for Aquaponics
- Energy Independence: One of the primary benefits of photovoltaic greenhouses is their ability to generate their own electricity. This energy independence can significantly reduce operational costs, especially in areas with high electricity prices or limited access to reliable power sources.
- Sustainability: Photovoltaic greenhouses promote sustainability by reducing reliance on non-renewable energy sources. The combination of solar power and aquaponics creates a farming system with a low carbon footprint, conserving both energy and water.
- Year-Round Production: The controlled environment inside a greenhouse allows for year-round production, regardless of external weather conditions. With solar panels providing consistent energy, even during less sunny seasons, the greenhouse can maintain optimal conditions for both plants and fish.
- Scalability: Photovoltaic greenhouses can be scaled to meet the needs of different operations, from small backyard systems to large commercial farms. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications and geographic locations.
- Economic Viability: While the initial investment in photovoltaic panels and greenhouse construction can be significant, the long-term savings in energy costs and the potential for increased yields can make the system economically viable. Additionally, surplus electricity can sometimes be sold back to the grid, providing an additional revenue stream.
Challenges and Considerations
While photovoltaic greenhouses offer many benefits, there are also challenges to consider. The efficiency of the solar panels and their placement must be carefully managed to ensure that enough light reaches the plants inside the greenhouse. Transparent or semi-transparent solar panels can mitigate this issue, but they may also be less efficient at generating electricity compared to traditional panels.

Moreover, the initial cost of installing photovoltaic systems can be high. However, as solar technology continues to advance and become more affordable, this barrier is gradually decreasing.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic greenhouses represent a promising innovation in the field of sustainable agriculture. By harnessing the power of the sun not only to grow plants but also to generate the energy needed to run essential systems like aquaponics, these greenhouses can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient food production system. As technology advances and the world continues to seek out renewable energy solutions, photovoltaic greenhouses will likely play an increasingly important role in the future of farming.