Nitrogen Cycle in Aquaponics/Sandponics
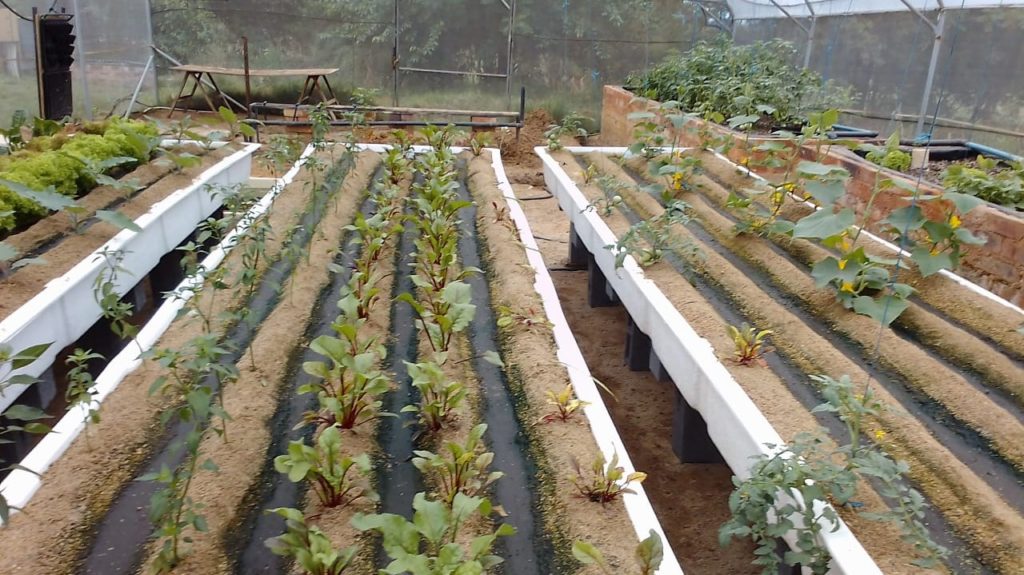

Aquaponics is a sustainable and efficient farming method that combines aquaculture (the raising of aquatic animals) with hydroponics (the growing of plants without soil). In an aquaponic system, fish waste provides the nutrients needed for plant growth. The nitrogen cycle plays a crucial role in this system, as it converts fish waste into a form that can be used by plants.
The Nitrogen Cycle
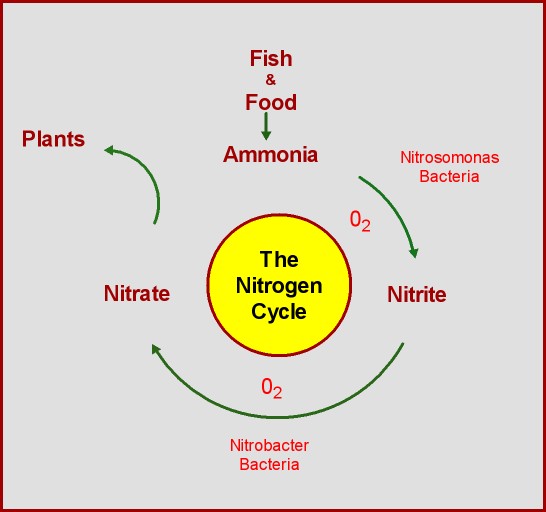
The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen is converted into different chemical forms in the environment. Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and is often the limiting factor in plant growth. In an aquaponic system, the nitrogen cycle involves the conversion of ammonia (NH3) to nitrite (NO2-) and then to nitrate (NO3-).
- Ammonia Production
In an aquaponic system, fish produce ammonia as a waste product. Ammonia is highly toxic to fish and must be removed from the water to maintain healthy fish. Beneficial bacteria, known as nitrifying bacteria, convert the ammonia into nitrite.
- Nitrite Production
Nitrite is less toxic than ammonia, but it can still harm fish at high levels. Nitrite is converted into nitrate by another type of beneficial bacteria, known as nitrite-oxidizing bacteria.
- Nitrate Production
Nitrate is the final product of the nitrogen cycle and is the form of nitrogen that plants can use. Plants take up nitrate through their roots and use it to build proteins and other essential compounds. Nitrate is also relatively harmless to fish at low levels, but high levels can still be toxic.
Maintaining the Nitrogen Cycle in Aquaponics
Maintaining the nitrogen cycle in aquaponics is critical for the health of both the fish and plants. The following are some tips for keeping the nitrogen cycle balanced:
- Monitor Water Parameters
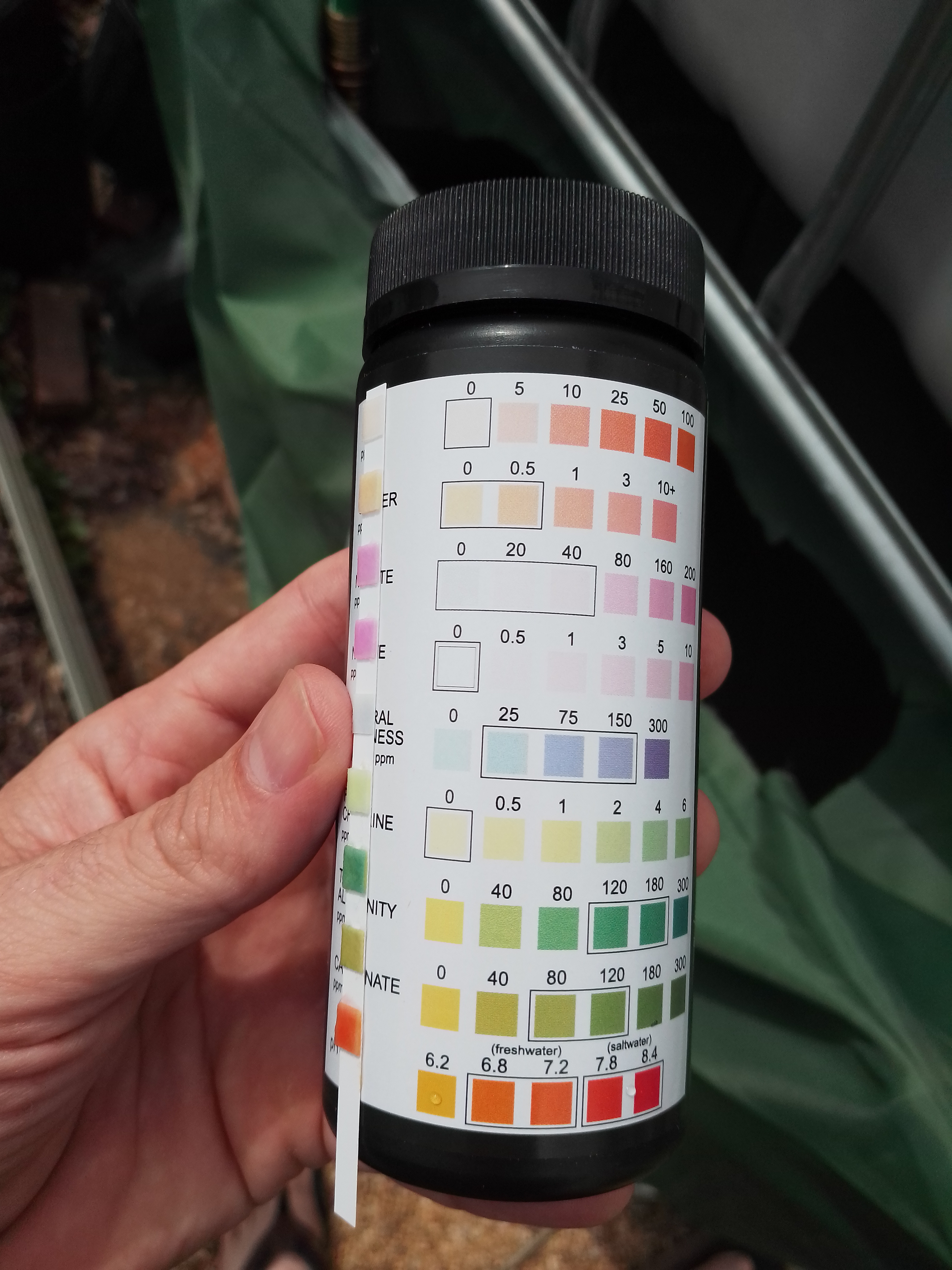
Regularly monitoring water parameters such as pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels is crucial to maintaining the nitrogen cycle in aquaponics. You can get aquarium test strips on Amazon for this purpose. Fish waste and uneaten fish food can produce excess ammonia, which can harm fish and disrupt the nitrogen cycle.
- Stocking Density
The stocking density of fish in an aquaponic system should be carefully monitored to prevent overloading the system with fish waste. Overstocking can lead to excess ammonia and nitrite levels, which can be harmful to fish and plants.
- Beneficial Bacteria
The beneficial bacteria that drive the nitrogen cycle in aquaponics need time to establish themselves. New aquaponic systems may require a few weeks to build up sufficient populations of nitrifying bacteria. Adding bacterial supplements can help speed up this process.
Conclusion
The nitrogen cycle is a crucial process in aquaponics that converts fish waste into a form that can be used by plants. By carefully monitoring water parameters, stocking density, and encouraging beneficial bacteria, aquaponic farmers can maintain a healthy and balanced nitrogen cycle. This leads to healthy fish and thriving plants, making aquaponics a sustainable and efficient farming method.